Learn how to read crypto charts - ultimate guide part 2.
In the second part of our ultimate guide to reading crypto charts, we'll take a closer look at some of the most popular charting tools and how to use them to your advantage. We'll also cover some basic technical analysis concepts and strategies that can help you make better informed trading decisions.
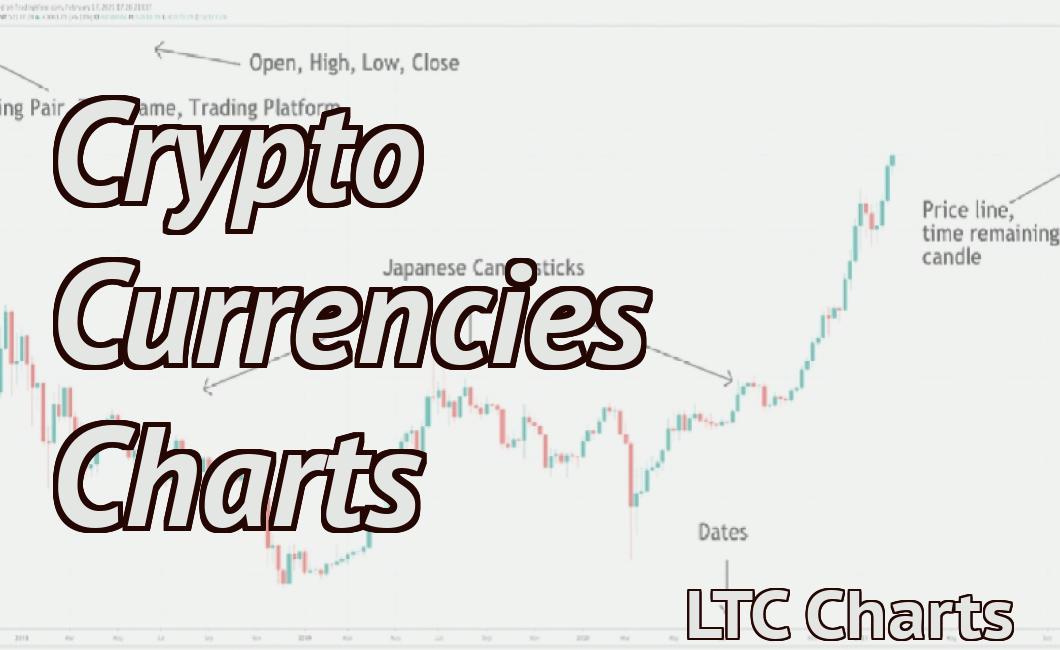
How to Read a Bar Chart
To read a bar chart, you first need to understand what it is. A bar chart is a graphical representation of data that shows how many items are in a particular category. The bars on the graph represent the number of items in that category.
To read a bar chart, you first need to understand what it is. A bar chart is a graphical representation of data that shows how many items are in a particular category. The bars on the graph represent the number of items in that category.
The height of the bar represents the quantity of that item in that category. The longer the bar, the more items in that category. The width of the bar represents the percentage of that item in that category. The closer the bar is to the center, the more evenly that category is divided.
How to Read a Candlestick Chart
The candlestick chart displays the performance of a security over a given period of time. The different types of candlesticks correspond to different types of data. The three basic types of candlesticks are open, close, and high/low. Each type of candlestick has its own specific meaning and use.
To read a candlestick chart, first identify the type of candlestick being displayed. Open, close, and high/low candlesticks are all displayed as circles. Next, identify the period of time being displayed. Each candlestick chart is usually divided into three periods: morning, noon, and night. Finally, identify the price points at which the candlestick was drawn. This information can be found on the left-hand side of the candlestick chart.
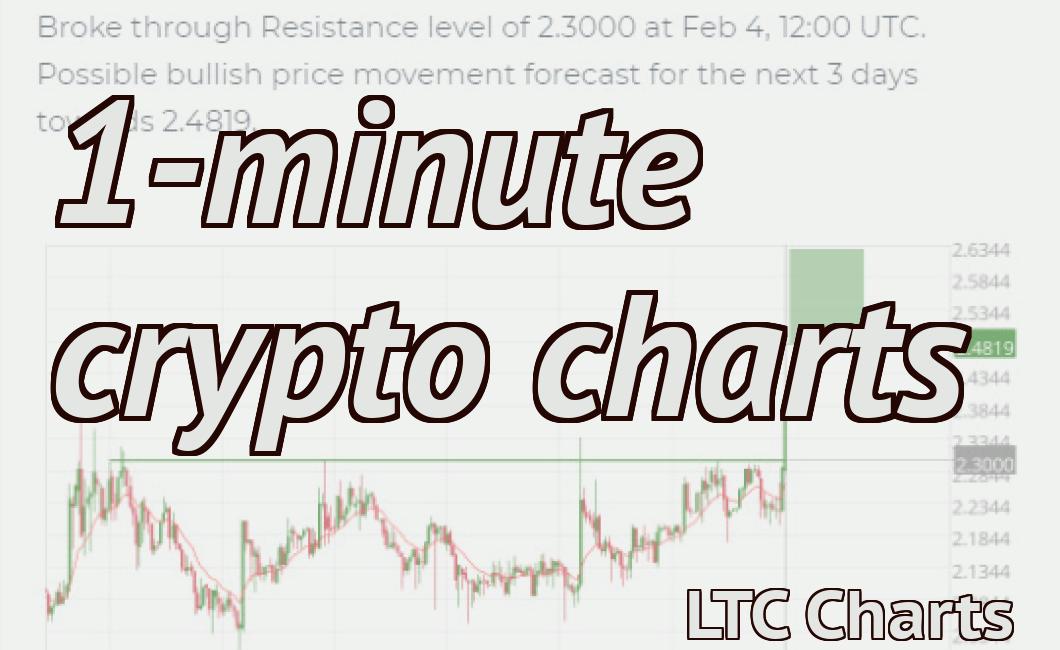
How to Read a Line Chart
A line chart is a graphical representation of data that shows the change in a particular variable over time. The horizontal axis (x-axis) typically shows time, while the vertical axis (y-axis) shows the value of the variable. Lines can be drawn to show the change in the variable over time.
How to Read a Cross Section Chart
Reading a cross section chart is a quick way to get a general overview of the company's financial performance.
The horizontal axis shows how much money the company made in each category, while the vertical axis shows how much money the company spent in each category.
The first thing to look for on a cross section chart is the trend line. This line shows how the company's performance has changed over time.
If you want to see more detail, you can look at the individual bars in each category. You can also use the chart to figure out where the company is spending its money and where it's making money.
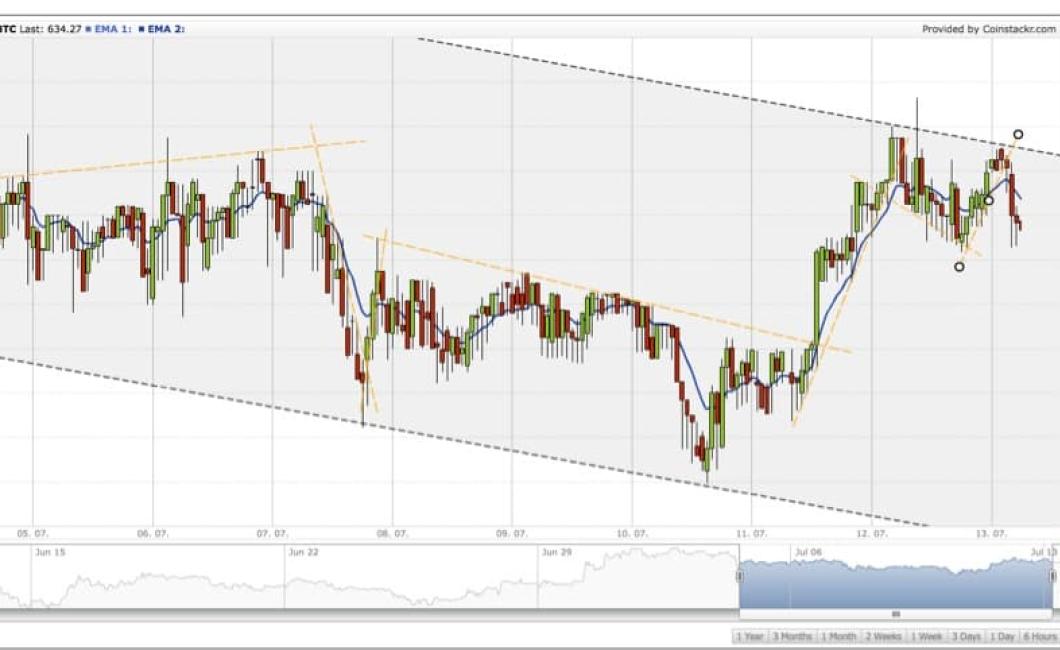
How to Read an Order Book
When you are looking to trade stocks, an order book is a valuable resource. An order book is a list of all the orders that have been placed for a particular stock. The order book is updated every time a trade is made, so you always know which stocks are being actively traded.
To read an order book, start by finding the symbol of the stock you are interested in. After the symbol, find the "quote" column. This column shows the current price of the stock. Next, find the "bid" and "ask" columns. The "bid" column shows the highest price that someone is willing to buy the stock at, and the "ask" column shows the lowest price that someone is willing to sell the stock at.
Next, find the number of shares that are being traded. This number will be listed next to the "volume" column. The "volume" column shows how many shares have been traded so far today. Finally, find the "price" column. This column shows the current price of the stock.
How to Read a Depth Chart
To read a depth chart, you first need to understand what it is. A depth chart is a visual representation of the organizational hierarchy in an organization. It shows the relative positions of employees within the organization, and how those positions are related to one another.
Each horizontal row on the chart represents a level of the organizational hierarchy. The leftmost column represents the lowest level of the hierarchy, and the rightmost column represents the highest level. The positions in between are represented by the vertical lines that run through the chart.
The distance between any two points on the chart is represented by the number in between those points. For example, the point at the bottom of the chart representing Level 2 is two levels above Level 1, and the point at the top of the chart representing Level 5 is five levels above Level 4.
Each employee's position on the chart is shown in two colors: green for Levels 1-3, and blue for Levels 4-6. The color of an employee's position indicates their relative rank within the organization. For example, an employee who is at Level 4 on the chart is four levels below the position of Level 1, and is therefore blue on the chart.
To read a depth chart, start at the bottom of the chart and work your way up. Each position on the chart will be represented by a number, and the position of each employee will be shown in blue and green. The distance between any two points on the chart will be shown in between those points in parentheses.
How to Read a Ticker Tape
Before you read a ticker tape, you will need to gather some information. This includes the company's name, ticker symbol, and stock price.
Next, you will need to find the "Open" and "High" prices for the day. The "Open" price is the price at which the stock was first sold to the public. The "High" price is the highest price that the stock has ever been sold at.
After you have gathered the information, you can begin to read the ticker tape. The ticker tape will list the name of the company, the ticker symbol, the stock price, and the number of shares that are available.
How to Read an Indicator
To read an indicator, you first need to identify the type of indicator. There are three types of indicators: moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), and MACD.
Moving Averages
Moving averages are a type of indicator that plots the average price of a security over a certain period of time. The indicator helps traders identify how volatile the price of the security has been over the past period of time.
To use a moving average, you need to identify the type of Moving Average (MA). There are three types of MA's: Simple Moving Average (SMA), Exponential Moving Average (EMA), and Weighted Moving Average (WMA).
Simple Moving Average (SMA)
The Simple Moving Average is the most common type of MA. It plots the average price of a security over a set period of time and updates the average every day. The SMA is calculated using the following formula:
SMA=MA(n-1)+MA(n-2)
where, MA(n) is the closing price of the security on day n, and n is the number of days in the period.
Exponential Moving Average (EMA)
The Exponential Moving Average is similar to the SMA, but it uses an exponential formula to calculate the average. The EMA is calculated using the following formula:
EMA=MAX(MA(n-1),MA(n-2))*100
where, MA(n) is the closing price of the security on day n, and n is the number of days in the period.
Weighted Moving Average (WMA)
The Weighted Moving Average is similar to the EMA, but it uses a weighting scheme to calculate the average. The WMA is calculated using the following formula:
WMA=MIN(EMA,MAX(MA(n-1),MA(n-2)))*100
where, MA(n) is the closing price of the security on day n, and n is the number of days in the period.
How to Use Technical Analysis
Technical analysis is the use of charts, indicators and other technical tools to help predict future price movements. Technical analysis can be used to identify trends and opportunities in the market, and to make informed investment decisions.
Technical analysis can be used to identify trends and opportunities in the market, and to make informed investment decisions.
Some common technical analysis tools include:
Charts: Charts are a useful way to visually display information. They can show market trends, price movement over time and other related information.
Indicators: Indicators are mathematical formulas that are used to predict future price movements. They can be used to identify patterns in market activity, and to make informed investment decisions.
Trading Rules: Trading rules are specific instructions that traders use to trade the markets. These rules may include guidelines for when to buy or sell assets, and how much money to put into a trade.